MVP in Software Development: Basics You Need to Know
Learn how to build a successful MVP in software development with clear steps, tools, & strategies to validate your idea fast & cut risks
Building a new app or product is exciting, but it is also risky. Many ideas fail because they reach the market too late or do not solve a real problem. That is where an MVP comes in.
MVP stands for Minimum Viable Product. It is the first working version of your software that includes only the most important features. The goal is simple - get feedback from users fast before spending too much time or money.
In software development an MVP helps test ideas in the real world. It is not about perfection. It is about proving whether your idea works. The MVP software development process is based on real feedback, not guesses.
This guide explains how MVPs work, why they matter, what tools you need, and how to build one step by step. You will also learn about MVP development stages, cost, and how big brands used MVPs to grow.
What is an MVP?
An MVP (Minimum Viable Product) is a version of a product that has just enough features to attract early users and collect feedback. It is not your final product. It is a learning tool.
Think of it as the smallest version of your idea that can stand on its own. You don’t add every feature - just the ones that show the product’s value.
Many confuse an MVP with a prototype. A prototype shows what the product could look like. It is used for design and concept testing. An MVP, on the other hand, is functional. Users can actually use it and give feedback. That is the big difference between prototype vs MVP.
Software MVP examples include companies like Dropbox and Airbnb. Dropbox first showed a simple video demo of how their syncing worked. It was not even a full product yet. People loved the idea, so they built it for real.
Airbnb started by renting their own apartment with a basic website. That small step helped them confirm that people were open to renting rooms from strangers.
Why Need MVP?
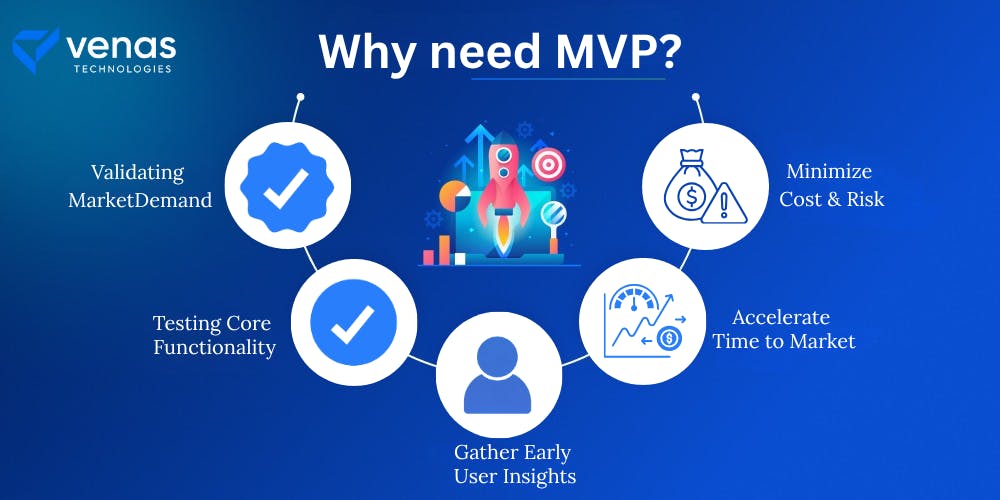
Every new software project starts with a guess - Will people want this? An MVP helps you answer that question early and safely. Here is why it is essential.
Validating Market Demand
You might think your idea is great. But do others agree? An MVP helps you check if people actually want your product. You test your idea in the real market before going all in.
Testing Core Functionality
Instead of building everything, focus on what matters most. An MVP helps test your product’s main function. If that core feature fails, you know early without wasting effort on extras.
Gather Early User Insights
An MVP lets you see how people use your product. You will discover what they like, what confuses them, and what they wish was different. This feedback shapes your next steps.
Accelerate Time to Market
You don’t need to wait for perfection. With an MVP, you can launch fast. It helps you reach real users sooner and adapt faster than competitors.
Minimize Cost & Risk
Full-scale products take time and money. An MVP lowers both. You invest less upfront and learn faster. If the idea fails, your loss is small. If it succeeds, you scale up with confidence.
The MVP Software Development Process Explained
The MVP software development process follows a clear path. You start small, test, learn, and grow. The goal is not just building software. It is building the right software.
It uses principles from the lean startup methodology, which focuses on testing ideas quickly and improving based on user feedback.
Here is how the process works step by step.
Stage 1: Ideation and Market Research
Every MVP starts with an idea. But ideas are worthless if no one needs them. You begin by researching your target audience.
Ask questions like:
- What problem am I solving?
- Who faces this problem most often?
- How do they solve it today?
Use surveys, interviews, or online forums to gather insights. Analyze competitors to see what is missing in their products.
Market research confirms whether your idea has real potential. It saves you from building something no one wants.
Stage 2: Building the MVP Roadmap
Once you understand your audience, create a roadmap. This is your plan for what to build first.
Define the core goal of your MVP. Then list all possible features. Separate them into two groups:
Must-have: features needed to show product value
Nice-to-have: features you can add later
Decide which features make it to version one. Each should directly support your main goal.
Map out the user journey - from sign-up to success. This keeps your MVP focused and usable.
Stage 3: Design and Prototype Creation
Before coding, design your MVP. This includes creating wireframes and prototypes to visualize how users will interact with your product.
Use tools like Figma, Adobe XD, or Sketch. They make it easy to design and test ideas quickly.
A prototype helps you catch design issues early. You can share it with users or your team to get feedback before development starts.
The focus at this stage is usability and clarity. Keep it simple. Each screen should guide the user toward one main action.
Stage 4: MVP Development Stages and Lifecycle
Now comes the coding part. The MVP development lifecycle usually follows an agile MVP development approach. That means building in small steps called sprints.
Developers build, test, and improve the product continuously. Each sprint adds or refines a feature.
Popular frameworks for MVP app development include Flutter, React, and Angular. These allow you to build apps quickly for web and mobile.
During this stage, focus on stability and performance, not perfection. The product should work well enough for users to test it and share honest feedback.
Stage 5: Testing, Feedback, and Iteration
Testing comes right after development. This is where you check if everything works as expected.
Use tools like JUnit for unit testing, Postman for API testing, and Selenium for automated browser tests.
After internal testing, share the MVP with a small group of users. Collect their opinions through surveys, interviews, or analytics tools.
Use that feedback to fix problems and improve the experience. This loop of testing and refining continues until you are confident in your product’s direction.
Essential Tools for MVPs
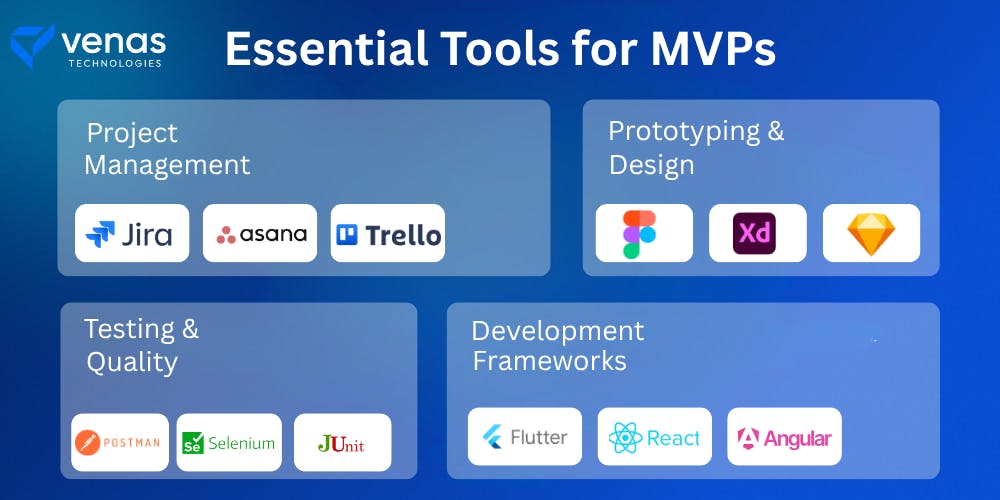
Building an MVP is easier when you have the right tools. Here is what helps at each stage.
Project Management: Use Jira, Trello, or Asana to plan tasks, track progress, and manage deadlines. They help your team stay organized and focused.
Prototyping & Design: Design tools like Figma, Adobe XD, and Sketch are perfect for wireframes and mockups. They make it easy to create user-friendly designs and share them for feedback.
Development Frameworks: Choose frameworks that speed up coding. Flutter, Building an MVP is easier when you have the right tools. Here is what helps at each stage.
Project Management: Use Jira, Trello, or Asana to plan tasks, track progress, and manage deadlines. They help your team stay organized and focused.
Prototyping & Design: Design tools like Figma, Adobe XD, and Sketch are perfect for wireframes and mockups. They make it easy to create user-friendly designs and share them for feedback.
Development Frameworks: Choose frameworks that speed up coding. Flutter, React, and Angular are popular because they let you build fast and deploy across platforms.
Testing & Quality: For quality checks, use JUnit, Postman, and Selenium. These tools ensure your product works smoothly before launch.
Each tool supports a key part of the MVP software development process - from idea to final test., and Angular are popular because they let you build fast and deploy across platforms.
Testing & Quality: For quality checks, use JUnit, Postman, and Selenium. These tools ensure your product works smoothly before launch.
Each tool supports a key part of the MVP software development process - from idea to final test.
MVP Development Cost and Timeline
The cost and time to build an MVP depend on the size of your project, the team, and the tools you use. But the rule is simple - start small.
A basic MVP can take anywhere from 4 to 12 weeks to build. The more features you add, the longer it takes.
If you hire a small team or agency, you might spend between $5,000 and $50,000. Larger or complex apps may go beyond that range.
Here is what affects cost and timeline
- Feature count: More features mean more time and expense
- Design complexity: A simple design is faster and cheaper
- Tech stack: Some frameworks cost less to maintain
- Team location: Rates differ between countries
- Testing needs: Extra testing adds to the timeline
The goal is not to make it cheap – it is to make it smart. Spend wisely on what proves your idea works. Once you get user feedback and traction, you can scale up your investment.
MVP vs Full Product: Key Differences
Many new founders think an MVP and a full product are the same. They are not. They serve different purposes.
An MVP is your first working version. It includes only essential features that solve a single core problem. It is built to test ideas fast.
A full product is what you create after validating the MVP. It has more features, a polished design, and advanced performance.
Here is a quick comparison:
Aspect | MVP | Full Product |
Purpose | Test idea | Scale validated idea |
Features | Only core ones | All planned features |
Speed | Fast to build | Takes longer |
Users | Early adopters | Broad audience |
Cost | Low | Higher |
Start small, learn what works, then scale. That is the logic behind MVP app development.
How MVP Supports Product Validation
The most powerful part of the MVP model is product validation. You can learn what customers want before investing heavily.
When users interact with your MVP, you get real data. You see which features they use most and what they ignore. That data drives smart decisions.
With the lean startup methodology, you test, measure, and improve fast. Each version gets closer to what people truly need.
MVPs keep you flexible. Instead of guessing, you respond to facts. You can change direction quickly if something doesn’t work. This agility saves both time and money.
Common Mistakes to Avoid in MVP Development
Even with a clear plan, it is easy to make mistakes when creating an MVP. These are the most common ones - and how to avoid them.
- Building too many features Focus only on what defines your idea. Extra features slow you down and distract from your goal.
- Ignoring user feedback Your MVP is built for learning. If you don’t listen to users, you miss the whole point.
- Poor testing Skipping testing can ruin even simple MVPs. Bugs and crashes drive users away fast. Always test before launch.
- Not defining success Set clear metrics from day one. Know how you will measure success - sign-ups, downloads, or engagement.
- Quitting too early Early feedback can be harsh. That is normal. Learn from it and adjust instead of giving up.
Avoiding these mistakes will save you time and frustration later.
Future Trends in MVP App Development
MVP development is changing as technology evolves. New tools and methods make it faster and smarter.
Here are some key trends shaping the future:
AI-driven MVPs: Artificial intelligence can help predict user needs, automate testing, and generate prototypes faster.
Low-code and no-code platforms: You can now build MVPs without deep coding skills. Tools like Bubble and Adalo let startups test ideas quickly.
Smarter analytics: Modern analytics tools give deep insight into how users behave. They help refine your MVP faster with real data.
Cross-platform development: Frameworks like Flutter and React Native let you build once and launch everywhere - web, iOS, and Android.
These trends make MVP app development more accessible, faster, and cheaper than ever before.
Conclusion: Why Every Startup Needs an MVP Strategy
An MVP is not just a smaller version of your product. It is a smarter way to start.
It helps you test your idea, get real feedback, and grow in the right direction. You learn what users want before spending big.
With the right tools and mindset, anyone can build an MVP. Start with a problem worth solving, keep it simple, and launch early.
The faster you learn, the faster you succeed.
FAQs about MVP in Software Development
1. What is the main purpose of MVP in software development? It helps test an idea early, get real user feedback, and reduce risk before building the full version.
2. How long does the MVP development lifecycle usually take? Most MVPs take 1 to 3 months to build, depending on complexity and team size.
3. What are the essential tools for MVP software development? You can use Jira or Trello for management, Figma for design, Flutter or React for coding, and Selenium or Postman for testing.
4. What is the difference between prototype vs MVP? A prototype is for visual testing. An MVP is functional and built for real users to try.
5. Can an MVP help in attracting investors? Yes. A working MVP proves your idea’s potential, which builds trust with investors.
Table of Contents
Related posts

business app development services
Business Mobile App Development: Best Strategies for 2026

Business Technology
The Digital Advantage: Why Companies That Invest in Smart Software Win Faster

custom software solutions
The Role of a Software Company in Ethiopia in Digital Transformation and Business Growth
Subscribe to our blogs to keep informed with as about technology.